Our academic staff are active and excellent in research. Our research areas include:
- Cell Biology
- Environmental Science
- Food & Nutritional Sciences
- Genomics and bioinformatics
- Marine Science
- Plant & Agricultural Science
- Physiology & Developmental Biology
- Protein Science
- Toxicology
The School also manages various research centers including:
- Centre for Cell and Developmental Biology
- Food Research Centre of The Chinese University of Hong Kong
- Simon FS Li Marine Science Laboratory
- The Centre for Protein Science and Crystallography
- The Croucher Laboratory for Human Genomics
- The Hong Kong Bioinformatics Centre
- UGC-AoE Centre for Plant & Agricultural Biotechnology

| Our research in Cell Biology covers a wide variety of research themes including apoptosis, cell structure and function, cell signaling, stem cell biology, neurobiology etc. The basic principles and questions in the fields are explored by using well-recognized cell systems, top model organisms and a variety of advanced technologies. |  |
|
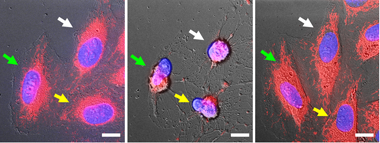
Cancer cells were discovered to be capable of recovering after exposure to a chemical cocktail which triggers apoptosis -- a cell suicide process. This finding could potentially help the development of new, more effective anti-cancer drugs. |
|
 |
 |
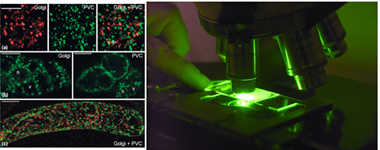
Confocal microscopy and transgenic tobacco cell lines were used to study protein trafficking and cell organelles in plants |
|
26 October 2012 CUHK Students Win Gold Medal at iGEM Asia Again Following last year's success, the iGEM (international Genetic Engineered Machine) team of The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) has won a gold medal again at the iGEM Asia Regional Jamboree, and is qualified to participate in the iGEM World Jamboree to be held at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology next month. The team consists of 9 students from the School of Life Sciences, 6 students from the Faculty of Engineering and 5 instructors. Since this May, the CUHK team had been devoted to preparing for the competition and developed the project completely by themselves, from defining themes, designing experiments to developing new parts and models from scratch. They demonstrated ample team spirit and efforts included publishing a wiki page, producing posters and introducing the project and the new devices on public occasions. In their award-winning project 'Light of No Return', the CUHK team has created bacteria harbouring rhodopsin to attract cells with different light spectra for cell sorting. The idea is to allow bacteria to 'see' and sense light source, so that light could be used to attract or separate bacteria. This technology may be used to improve the efficacy of chemical treatment such as water sewage treatment. The team has also successfully made new biobricks with introduce 'bacterial killing' DNA to enhance biosafety. These bacterial killing biobricks can enhance biosafety by preventing the proliferation of transformed bacteria and antibiotic resistant bacteria, which are also known as the super bugs. For details of the project, please visit the following links: In addition, members of the CUHK team also organized various high school outreach activities to introduce to high school students the potential social implications and significance in academic research of genetic engineering and synthetic biology through talks and workshops, with an aim to enhance their understanding and to raise their interests in this field. The team will also introduce synthetic biology and their project to the public at the University's Orientation Day on coming Saturday (27 October). About iGEM Competition iGEM is an annual premier synthetic biology competition for undergraduates worldwide. It was established by the MIT in 2004 to foster students’ learning in synthetic biology, promote collaboration among students and nurture biology talents. Participating teams are required to specify, design, build, and test simple biological systems made from standard, interchangeable biological parts. The accomplishments of these student teams often lead to important advances in medicine, energy, and the environment. For more information, please visit http://www.igem.org. 二零一二年十月二十六日
中大生再奪國際遺傳工程機器設計競賽亞洲區金獎 香港中文大學(中大)遺傳工程機器隊伍延續去年佳績,日前在國際遺傳工程機器設計競賽(iGEM)亞洲區比賽中再奪金獎,並將於下月赴美國麻省理工學院參加世界決賽。中大隊伍由9名生命科學學院的學生、6名工程學院學生及5名教練組成。他們自今年五月起已積極作好準備,由訂定題目到創造生物零件及模型,以及設計實驗,皆完全由學生自行創作。在亞洲區比賽當天,各隊員分工合作,除完成實驗外,還要製作網頁及海報,並在公開演說中講解其創作的課題,終獲得理想成績。 中大隊伍的參賽研究項目名為「見光不回頭」 (Light of No Return)。隊員別具創意,利用能夠辨別顏色的蛋白注入細菌內,把不能看東西的細菌加上可感光的「眼睛」。此構思可利用不同光譜吸引或者分離細菌,有助污水處理如吸收污染物或提高分解污染物的效益。中大隊伍同時引進了能注入基因片斷進行殺菌的新生物零件,提高生物安全性,可防止抗藥惡菌肆虐,亦可阻止轉基因細菌擴散,具醫療應用的價值。有關研究項目的詳細內容,可參考以下連結: 此外,參賽隊伍成員於比賽後亦舉辦了中學外展活動,透過講座及實驗工作坊向高中生介紹遺傳工程及合成生物學技術,及其對社會或學術研究的貢獻,加深他們對此學科的興趣。隊員亦將於本周六(10月27日)舉行的本科生入學資訊日向公眾介紹有關知識。 iGEM比賽簡介 iGEM比賽為國際合成生物學界每年一度的盛事,專為本科生而設。iGEM由麻省理工學院於2004年創立,旨在促進學生在合成生物學的學習、交流與合作,以培養合成生物學人才。比賽隊伍須利用基本且可交替的生物部件,設計及建立有效的生物系統。參賽作品水平超卓,有效推動醫學、能源及環境等方面的發展。網址:http://www.igem.org。
|
|
|
| >>iGEM 2012 CUHK Team Website |
| >>Team Members |
| >>Photo Albums Videos: i. Presentation ii. Q & A |
|
26 October 2012 CUHK Students Win Gold Medal at iGEM Asia Again Following last year's success, the iGEM (international Genetic Engineered Machine) team of The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) has won a gold medal again at the iGEM Asia Regional Jamboree, and is qualified to participate in the iGEM World Jamboree to be held at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology next month. The team consists of 9 students from the School of Life Sciences, 6 students from the Faculty of Engineering and 5 instructors. Since this May, the CUHK team had been devoted to preparing for the competition and developed the project completely by themselves, from defining themes, designing experiments to developing new parts and models from scratch. They demonstrated ample team spirit and efforts included publishing a wiki page, producing posters and introducing the project and the new devices on public occasions. In their award-winning project 'Light of No Return', the CUHK team has created bacteria harbouring rhodopsin to attract cells with different light spectra for cell sorting. The idea is to allow bacteria to 'see' and sense light source, so that light could be used to attract or separate bacteria. This technology may be used to improve the efficacy of chemical treatment such as water sewage treatment. The team has also successfully made new biobricks with introduce 'bacterial killing' DNA to enhance biosafety. These bacterial killing biobricks can enhance biosafety by preventing the proliferation of transformed bacteria and antibiotic resistant bacteria, which are also known as the super bugs. For details of the project, please visit the following links: In addition, members of the CUHK team also organized various high school outreach activities to introduce to high school students the potential social implications and significance in academic research of genetic engineering and synthetic biology through talks and workshops, with an aim to enhance their understanding and to raise their interests in this field. The team will also introduce synthetic biology and their project to the public at the University's Orientation Day on coming Saturday (27 October). About iGEM Competition iGEM is an annual premier synthetic biology competition for undergraduates worldwide. It was established by the MIT in 2004 to foster students’ learning in synthetic biology, promote collaboration among students and nurture biology talents. Participating teams are required to specify, design, build, and test simple biological systems made from standard, interchangeable biological parts. The accomplishments of these student teams often lead to important advances in medicine, energy, and the environment. For more information, please visit http://www.igem.org. 二零一二年十月二十六日
中大生再奪國際遺傳工程機器設計競賽亞洲區金獎 香港中文大學(中大)遺傳工程機器隊伍延續去年佳績,日前在國際遺傳工程機器設計競賽(iGEM)亞洲區比賽中再奪金獎,並將於下月赴美國麻省理工學院參加世界決賽。中大隊伍由9名生命科學學院的學生、6名工程學院學生及5名教練組成。他們自今年五月起已積極作好準備,由訂定題目到創造生物零件及模型,以及設計實驗,皆完全由學生自行創作。在亞洲區比賽當天,各隊員分工合作,除完成實驗外,還要製作網頁及海報,並在公開演說中講解其創作的課題,終獲得理想成績。 中大隊伍的參賽研究項目名為「見光不回頭」 (Light of No Return)。隊員別具創意,利用能夠辨別顏色的蛋白注入細菌內,把不能看東西的細菌加上可感光的「眼睛」。此構思可利用不同光譜吸引或者分離細菌,有助污水處理如吸收污染物或提高分解污染物的效益。中大隊伍同時引進了能注入基因片斷進行殺菌的新生物零件,提高生物安全性,可防止抗藥惡菌肆虐,亦可阻止轉基因細菌擴散,具醫療應用的價值。有關研究項目的詳細內容,可參考以下連結: 此外,參賽隊伍成員於比賽後亦舉辦了中學外展活動,透過講座及實驗工作坊向高中生介紹遺傳工程及合成生物學技術,及其對社會或學術研究的貢獻,加深他們對此學科的興趣。隊員亦將於本周六(10月27日)舉行的本科生入學資訊日向公眾介紹有關知識。 iGEM比賽簡介 iGEM比賽為國際合成生物學界每年一度的盛事,專為本科生而設。iGEM由麻省理工學院於2004年創立,旨在促進學生在合成生物學的學習、交流與合作,以培養合成生物學人才。比賽隊伍須利用基本且可交替的生物部件,設計及建立有效的生物系統。參賽作品水平超卓,有效推動醫學、能源及環境等方面的發展。網址:http://www.igem.org。
|
|
|
| >>iGEM 2012 CUHK Team Website |
| >>Team Members |
| >>Photo Albums Videos: i. Presentation ii. Q & A |
|
16 April 2014 CUHK MBTE Student Wins the Innovation and Technology Scholarship Award Scheme 2014 |




